Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is an infection spread by tick bites. Ticks that spread it are found in parts of Europe and Asia, and some parts of the UK.
Check if you could be at risk of TBE
The risk of getting TBE is very low.
Ticks that spread it can be found in:
- most of Europe – including parts of England
- Russia
- parts of China and Japan
Ticks live in forests and grassy areas. You're more at risk of being bitten if you do activities such as hiking and camping.
Not all ticks spread TBE. Even if you're bitten, the risk of getting seriously ill is low.
You can check the risks of a country you're travelling to on the Travel Health Pro website.
You can get vaccinated against TBE if you're at risk
Consider having the TBE vaccine if you're visiting a country where the infection is common and you're planning to do outdoor activities when you get there.
Two injections of the vaccine can protect you for about a year. A third injection can protect you for about 3 years.
You need to have the first injection at least 1 month before travelling.
The TBE vaccine is not available on the NHS. Search online for a travel clinic that offers it. It costs about £65 per injection.
How to avoid tick bites
Always try to avoid being bitten in places where ticks are found.
To reduce the risk of being bitten:
- cover your skin while walking outdoors and tuck your trousers into your socks
- use insect repellent on your clothes and skin – products containing DEET are best
- stick to paths whenever possible
- wear light-coloured clothing so ticks are easier to spot and brush off
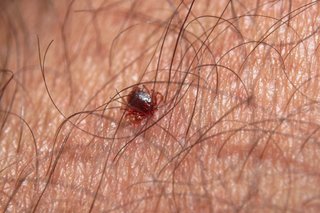
How to spot and remove ticks
Important
Tick bites are not always painful. You may not notice a tick unless you see it on your skin.
Always check your skin and hair after being outdoors.
SINCLAIR STAMMERS/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY

DR P. MARAZZI/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY

Shotshop GmbH / Alamy Stock Photo
To remove a tick safely:
- Use fine-tipped tweezers or a tick removal tool. You can buy these from some pharmacies, vets and pet shops.
- Grasp the tick as close to your skin as possible.
- Slowly pull upwards, taking care not to squeeze or crush the tick. Dispose of it when you have removed it.
- Clean the bite with antiseptic or soap and water.
The risk of getting ill is low. You do not need to do anything else unless you become unwell.
Non-urgent advice: See a doctor if:
You have been bitten by a tick or visited an area in the past month where ticks are found, and you get either:
- flu-like symptoms – such as feeling hot and shivery, headaches, aching muscles or feeling sick, or
- a circular red rash
Either of these could be an early sign of an infection.
Tell the doctor if you have been in forests or grassy areas.
Immediate action required: Go to hospital if you or someone else:
- gets a stiff neck and a severe headache
- gets pain when looking at bright lights
- has a fit (seizure)
- has a change in behaviour – such as sudden confusion
- develops weakness or loss of movement in part of the body
Page last reviewed: 9 April 2018
Next review due: 9 April 2021
