Scabies is very common and anyone can get it. It should be treated quickly to stop it spreading.
Check if it's scabies
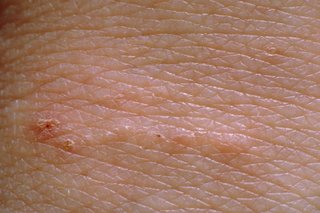
One of the first symptoms is intense itching, especially at night.
JOHN RADCLIFFE HOSPITAL/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
DR P. MARAZZI/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
DR P. MARAZZI/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
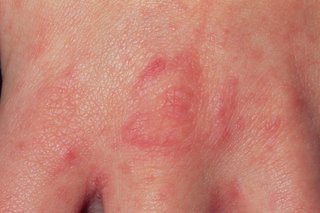
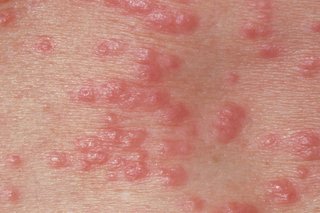
The scabies rash usually spreads across the whole body, apart from the head.
Elderly people, young children and those with a weakened immune system may also develop a rash on their head and neck.
When it's not scabies
Many other things can cause itchy skin and rashes in babies and children.
A pharmacist can help with scabies
Scabies is not usually a serious condition, but it does need to be treated.
A pharmacist will recommend a cream or lotion that you apply over your whole body. It's important to read the instructions carefully.
You'll need to repeat the treatment 1 week later.
Scabies is very infectious, but it can take up to 8 weeks for the rash to appear.
Everyone in the household needs to be treated at the same time, even if they do not have symptoms.
Anyone you have had sexual contact with in the past 8 weeks should also be treated.
Things you can do during treatment to stop scabies spreading
Do
-
wash all bedding and clothing in the house at 50C or higher on the first day of treatment
-
put clothing that cannot be washed in a sealed bag for 3 days until the mites die
-
stop babies and children sucking treatment from their hands by putting socks or mittens on them
Don't
-
do not have sex or close physical contact until you have completed the full course of treatment
-
do not share bedding, clothing or towels with someone with scabies
How long it takes to get rid of scabies
You or your child can go back to work or school 24 hours after the first treatment.
Although the treatment kills the scabies mites quickly, the itching can carry on for a few weeks.
Non-urgent advice: See a GP if:
- your skin is still itching 4 weeks after treatment has finished
Scabies can spread easily
Scabies are passed from person to person by skin-to-skin contact. You cannot get scabies from pets.
People who live or work closely together in nurseries, university halls of residence or nursing homes are more at risk.
Important
Anyone can get scabies. It has nothing to do with poor hygiene.
Complications of scabies
Scratching the rash can cause skin infections like impetigo.
Page last reviewed: 10 November 2017
Next review due: 10 November 2020
