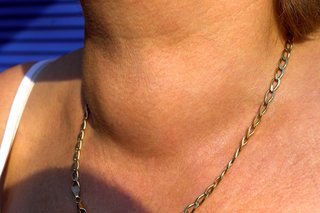
A goitre (sometimes spelled "goiter") is a swelling of the thyroid gland that causes a lump in the front of the neck. The lump will move up and down when you swallow.
Chris Pancewicz / Alamy Stock Photo
The thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped gland in the neck, just in front of the windpipe (trachea).
It produces thyroid hormones, which help regulate the body's metabolism, the chemical processes that occur in the body.
Symptoms of a goitre
The size of a goitre can vary from person to person. In most cases, the swelling is small and does not cause any symptoms.
In more severe cases, symptoms may include:
- coughing
- a tight feeling in your throat
- changes to your voice, such as hoarseness
- difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- difficulty breathing – there may be a high-pitched sound when you breathe
Diagnosing a goitre
See your GP if you think you have a goitre. They'll examine your neck to see whether your thyroid gland is swollen.
The GP may also request a thyroid function test to see how well your thyroid gland is working.
A thyroid function test measures the level of certain hormones in your blood.
It can show whether you have an underactive or overactive thyroid, both of which are associated with goitre.
If necessary, you may be referred to a specialist in hospital for further tests or treatment.
Treating a goitre
The treatment for a goitre depends on the underlying cause.
If the goitre is small and not causing any problems, a wait-and-see approach is usually recommended.
Other possible treatments include radioiodine treatment and thyroid surgery.
Although most goitres are non-cancerous, it's estimated that in 1 in 20 cases they may be a sign of thyroid cancer.
Causes of a goitre
A goitre can have several possible causes, including:
- an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism)
- an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism)
- hormone changes during puberty, pregnancy or the menopause
- not enough iodine in your diet
- taking some types of medicine, such as lithium, a medicine used to treat some mental health conditions
- an inflamed thyroid gland (thyroiditis)
- having radiation treatment to your neck or chest area, such as radiotherapy for neck cancer
- nodules or cysts within the thyroid – most are harmless, but they should be assessed
- thyroid cancer – a rare type of cancer in the UK
Anyone can develop a goitre, but the chances increase with age. Women are also more likely to develop a goitre.
Types of goitre
There are 2 main types of goitre:
- diffuse goitre – where the entire thyroid gland swells and feels smooth to the touch
- nodular goitre – where solid or fluid-filled lumps called nodules develop within the thyroid and make the thyroid gland feel lumpy to touch; the nodules can be single or multiple and may contain fluid
Page last reviewed: 15 April 2019
Next review due: 15 April 2022
